Wenn der untere Rücken streikt – ISG, Becken und Organe im Zusammenspiel
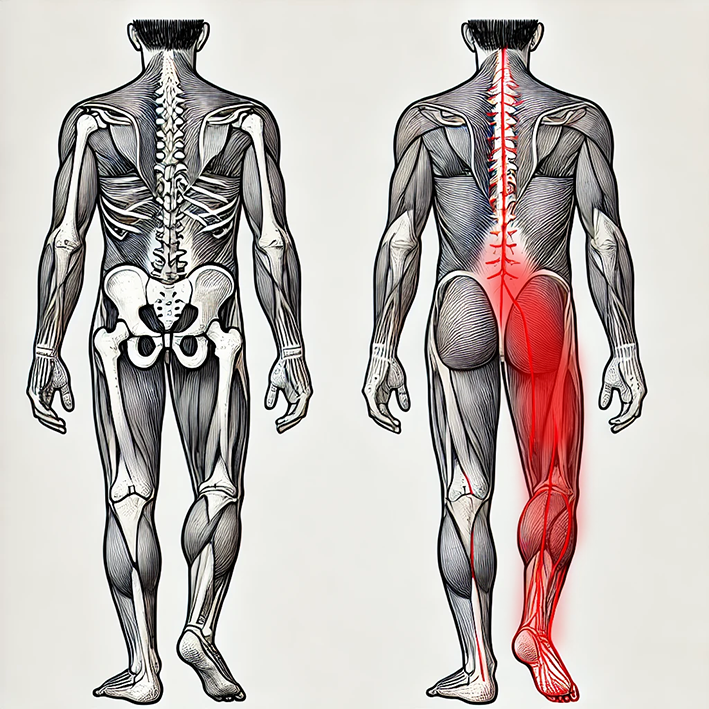
Viele Menschen leiden unter Schmerzen im unteren Rücken, im Bereich des Kreuzbeins (Sakrum) oder des Iliosakralgelenks (ISG). Diese Beschwerden treten häufig einseitig auf, ziehen in Gesäß oder Leiste und werden oft als „blockiert“ oder „instabil“ beschrieben. Doch was viele nicht wissen: Diese Region ist eng verbunden mit dem Beckeninneren – also Blase, Uterus, Prostata und Enddarm.
Organischer Zusammenhang: Beckenorgane und Lendenwirbelsäule
Die vegetative Versorgung von Blase, Gebärmutter, Prostata und Enddarm erfolgt segmental über die Nerven aus dem Bereich L4 bis S1 – also aus der unteren Lendenwirbelsäule bis hin zum Kreuzbein. Eine Blockade oder muskuläre Spannung in diesem Bereich kann daher nicht nur Rückenschmerzen verursachen, sondern auch funktionelle Störungen in den Organen des kleinen Beckens.
Mögliche internistische Symptome:
• Reizblase oder häufiger Harndrang
• Menstruationsbeschwerden, Unterbauchziehen
• Potenzstörungen, Erektionsprobleme
• Verstopfung, Druckgefühl im Enddarm
• Leistenschmerz, Unruhe im Becken
Diese Beschwerden entstehen oft nicht durch eine Erkrankung des Organs selbst, sondern durch eine gestörte nervale Ansteuerung – verursacht durch Fehlhaltung, emotionale Belastung oder Bewegungsmangel im Bereich der Lendenwirbelsäule.
Die emotionale Komponente: Sicherheit, Sexualität, Selbstvertrauen
Die Beckenregion steht symbolisch für:
• Vertrauen in den eigenen Körper
• Sicherheit in Beziehungen
• Sexualität, Fortpflanzung und Selbstannahme
• „Loslassen können“ – auch emotional
Chronischer Stress oder ungelöste innere Konflikte können genau hier Spannungen erzeugen – sichtbar als muskuläre Verkrampfung, Beckenbodenspannung oder ISG-Schmerz.
Physikalische Lösung mit dem mobiball
Der mobiball bietet eine einfache, effektive Möglichkeit zur Selbstbehandlung der unteren Wirbelsäule und des Kreuzbeins.
So funktioniert es:
• Platziere den mobiball im Bereich L1–L3 , während du dich auf einer Sitzlehne setzt.
• Verweile täglich 30–90 Minuten in aufrechter Position auf dem mobiball.
• Dabei kommt es zur sanften Mobilisierung und Druckentlastung der Nervenbahnen, die die Beckenorgane versorgen.
Was passiert im Körper?
• Die segmentale Versorgung verbessert sich,
• die Beckenorgane können wieder harmonisch arbeiten,
• Schmerzen im Kreuz, ISG oder Gesäß lösen sich schrittweise auf.
Fazit:
• Schmerzen im unteren Rücken haben oft tiefer liegende Ursachen,
• Die Verbindung zu Blase, Gebärmutter, Prostata oder Enddarm ist real,
• Der Körper meldet sich dort, wo mechanisch, vegetativ oder emotional etwas aus dem Gleichgewicht geraten ist,
• Mit dem mobiball kannst du gezielt Einfluss nehmen – ohne Medikamente, ohne Nebenwirkungen.
_________________________________________________________
English:
When the lower back gives out – ISG, pelvis, and organs working together
Many people suffer from lower back pain, especially in the sacral area (sacrum) or the sacroiliac joint (ISG). These issues often appear on one side, radiate into the buttocks or groin, and are commonly described as “blocked” or “unstable.” What many don't know: this area is closely connected to the inner pelvis – including the bladder, uterus, prostate, and rectum.
Organ connection: Pelvic organs and lumbar spine
The autonomic nerve supply to the bladder, uterus, prostate, and rectum is segmentally provided by nerves from the L4 to S1 region – meaning from the lower lumbar spine down to the sacrum. A blockage or muscular tension in this area can therefore not only cause back pain but also functional disorders in the pelvic organs.
Possible internal symptoms:
• Irritable bladder or frequent urination
• Menstrual pain, lower abdominal cramping
• Erectile dysfunction, potency issues
• Constipation, rectal pressure
• Groin pain, pelvic restlessness
These complaints often do not originate from a disease of the organ itself, but from disturbed nerve signaling – caused by poor posture, emotional stress, or lack of movement in the lumbar area.
The emotional component: safety, sexuality, self-confidence
The pelvic region symbolically represents:
• Trust in one’s own body
• Security in relationships
• Sexuality, reproduction, and self-acceptance
• The ability to “let go” – even emotionally
Chronic stress or unresolved inner conflicts can create tension here – visible as muscle tightness, pelvic floor tension, or ISG pain.
Physical solution with the mobiball
The mobiball provides a simple and effective method for self-treatment of the lower spine and sacrum.
How it works:
• Place the mobiball in the L1–L3 area while sitting on a firm chair.
• Stay seated upright on the mobiball for 30–90 minutes daily.
• This leads to gentle mobilization and pressure relief of the nerve pathways supplying the pelvic organs.
What happens in the body?
• Segmental nerve supply improves,
• Pelvic organs can function in harmony again,
• Pain in the sacrum, ISG, or buttocks gradually resolves.
Conclusion:
• Lower back pain often has deeper causes,
• The connection to bladder, uterus, prostate, or rectum is real,
• The body speaks where there is imbalance – mechanical, autonomic, or emotional,
• With the mobiball, you can influence this specifically – without medication, without side effects.
____________________________________________________________________________
فارسی
وقتی کمر پایین قفل میکند – همکاری مفصل خاجی خاصره (ISG)، لگن و اندامهای داخلی
بسیاری از افراد از درد در ناحیه پایین کمر، در ناحیه استخوان خاجی (ساکروم) یا مفصل ایلیوساکرال (ISG) رنج میبرند. این دردها اغلب یکطرفه هستند، به باسن یا کشاله ران کشیده میشوند و معمولاً بهصورت «قفلشده» یا «ناپایدار» توصیف میشوند. اما چیزی که بسیاری نمیدانند این است که این ناحیه با اندامهای داخل لگن – مثانه، رحم، پروستات و رکتوم – ارتباط نزدیکی دارد.
ارتباط اندامی: اندامهای لگنی و ستون فقرات کمری
تأمین عصبی خودکار مثانه، رحم، پروستات و رکتوم بهصورت بخشی از ناحیه عصبی L4 تا S1 انجام میشود – یعنی از مهرههای کمری پایینی تا ساکروم. بنابراین، انسداد یا تنش عضلانی در این ناحیه میتواند نه تنها باعث کمردرد شود، بلکه منجر به اختلالات عملکردی در اندامهای لگنی نیز گردد.
علائم ممکن از نظر داخلی:
• مثانه تحریکپذیر یا تکرر ادرار
• درد دوران قاعدگی، کشیدگی در ناحیه زیر شکم
• اختلالات جنسی، مشکلات نعوظ
• یبوست، احساس فشار در رکتوم
• درد کشاله ران، بیقراری لگنی
این علائم اغلب ناشی از بیماری اندامها نیستند، بلکه از اختلال در فرماندهی عصبی ناشی میشوند – که میتواند به دلیل وضعیت بدنی نامناسب، فشار روحی یا کمتحرکی در ناحیه کمر ایجاد شود.
جنبه احساسی: امنیت، تمایلات جنسی، اعتماد به نفس
ناحیه لگن بهطور نمادین نشاندهنده موارد زیر است:
• اعتماد به بدن خود
• احساس امنیت در روابط
• تمایلات جنسی، تولید مثل و پذیرش خود
• توانایی «رها کردن» – حتی به صورت احساسی
استرس مزمن یا تعارضات حلنشده درونی میتوانند دقیقاً در این ناحیه تنش ایجاد کنند – که بهصورت اسپاسم عضلانی، گرفتگی کف لگن یا درد ISG ظاهر میشود.
راهکار فیزیکی با mobiball
موبیبال یک روش ساده و مؤثر برای درمان خودکار ناحیه پایینی ستون فقرات و استخوان خاجی است.
نحوه استفاده:
• موبیبال را در ناحیه L1 تا L3 / ساکروم قرار دهید و روی یک صندلی بنشینید.
• روزانه به مدت ۳۰ تا ۹۰ دقیقه در وضعیت نشسته و صاف روی آن بمانید.
• این کار باعث تحرک ملایم و کاهش فشار از مسیرهای عصبی میشود که اندامهای لگنی را تغذیه میکنند.
چه اتفاقی در بدن میافتد؟
• تغذیه عصبی بهبود مییابد،
• اندامهای لگنی بهصورت هماهنگتر عمل میکنند،
• درد در ناحیه خاجی، ISG یا باسن بهتدریج کاهش مییابد.
نتیجه گیری:
• درد پایین کمر اغلب ریشههای عمیقتری دارد،
• ارتباط آن با مثانه، رحم، پروستات یا رکتوم واقعی است،
• بدن در جایی واکنش نشان میدهد که چیزی از نظر مکانیکی، عصبی یا احساسی از تعادل خارج شده،
• با موبیبال میتوانی بهصورت هدفمند تأثیر بگذاری – بدون دارو، بدون عوارض جانبی.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Español:
Cuando la zona lumbar se bloquea – Articulación sacroilíaca, pelvis y órganos en interacción
Muchas personas sufren de dolor en la parte baja de la espalda, en la zona del sacro o de la articulación sacroilíaca (ASI). Estas molestias suelen presentarse de un solo lado, irradiarse hacia el glúteo o la ingle y se describen frecuentemente como una sensación de "bloqueo" o "inestabilidad". Pero lo que muchos no saben es que esta región está estrechamente relacionada con los órganos internos de la pelvis: vejiga, útero, próstata y recto.
Relación orgánica: Órganos pélvicos y columna lumbar
La inervación vegetativa de la vejiga, el útero, la próstata y el recto se produce de forma segmentaria a través de los nervios que emergen de L4 a S1 – desde la parte baja de la columna lumbar hasta el sacro. Un bloqueo o una tensión muscular en esta zona puede provocar no solo dolor lumbar, sino también disfunciones en los órganos del suelo pélvico.
Síntomas internos posibles:
• Vejiga hiperactiva o necesidad frecuente de orinar
• Dolores menstruales, calambres en el bajo vientre
• Problemas de erección, disfunción eréctil
• Estreñimiento, sensación de presión rectal
• Dolor inguinal, inquietud pélvica
Estas molestias no se deben necesariamente a una enfermedad del órgano, sino a una alteración en la señalización nerviosa, causada por una mala postura, estrés emocional o falta de movimiento en la zona lumbar.
Componente emocional: seguridad, sexualidad, confianza
La región pélvica representa simbólicamente:
• Confianza en el propio cuerpo
• Seguridad en las relaciones
• Sexualidad, reproducción y autoaceptación
• Capacidad de “soltar” – también a nivel emocional
El estrés crónico o los conflictos internos no resueltos pueden generar tensión justo aquí – visible como contracción muscular, tensión del suelo pélvico o dolor en la ASI.
Solución física con el mobiball
El mobiball ofrece una forma sencilla y eficaz de automasajear y movilizar la zona lumbar y el sacro.
Cómo se utiliza:
• Coloca el mobiball en la zona de L1–L4 mientras te sientas en una superficie firme.
• Permanece sentado de forma erguida sobre el mobiball entre 30 y 90 minutos al día.
• Esto produce una movilización suave y alivia la presión sobre las vías nerviosas que controlan los órganos pélvicos.
¿Qué ocurre en el cuerpo?
• Mejora la inervación segmentaria
• Los órganos pélvicos vuelven a funcionar en armonía
• El dolor en el sacro, la ASI o los glúteos se alivia gradualmente
Conclusión:
• El dolor lumbar suele tener causas profundas
• La conexión con la vejiga, el útero, la próstata o el recto es real
• El cuerpo habla cuando algo está en desequilibrio – mecánico, nervioso o emocional
• Con el mobiball puedes actuar directamente – sin medicamentos y sin efectos secundarios
_________________________________________________________________________
Italiano:
Quando la zona lombare si blocca – Articolazione sacroiliaca, bacino e organi in sinergia
Molte persone soffrono di dolori nella parte bassa della schiena, nella zona del sacro o dell’articolazione sacroiliaca (SI). Questi disturbi si manifestano spesso da un solo lato, si irradiano ai glutei o all’inguine e vengono descritti come una sensazione di "blocco" o "instabilità". Tuttavia, ciò che molti non sanno è che questa zona è strettamente collegata agli organi interni del bacino: vescica, utero, prostata e retto.
Connessione organica: Organi pelvici e colonna lombare
L’innervazione vegetativa di vescica, utero, prostata e retto avviene in modo segmentario tramite i nervi della zona L4–S1 – dalla parte inferiore della colonna lombare fino al sacro. Un blocco o una tensione muscolare in questa regione può causare non solo dolore lombare, ma anche disfunzioni negli organi pelvici.
Possibili sintomi interni:
• Vescica iperattiva o stimolo frequente a urinare
• Dolori mestruali, crampi al basso ventre
• Disfunzione erettile o problemi di potenza
• Stitichezza, senso di pressione rettale
• Dolore inguinale, agitazione nel bacino
Spesso questi sintomi non dipendono da una patologia dell’organo stesso, ma da un’interferenza nella trasmissione nervosa, causata da cattiva postura, stress emotivo o sedentarietà nella zona lombare.
Componente emotiva: sicurezza, sessualità, fiducia in sé
La zona pelvica rappresenta simbolicamente:
• Fiducia nel proprio corpo
• Sicurezza nelle relazioni
• Sessualità, fertilità e autoaccettazione
• Capacità di “lasciar andare” – anche a livello emotivo
Lo stress cronico o i conflitti interiori irrisolti possono creare tensioni proprio qui – che si manifestano come contratture, tensione del pavimento pelvico o dolore all’SI.
Soluzione fisica con il mobiball
Il mobiball è uno strumento semplice ed efficace per il trattamento autonomo della zona lombare e del sacro.
Come funziona:
• Posiziona il mobiball nella zona tra L1 e L3 mentre sei seduto.
• Rimani seduto in posizione eretta sul mobiball per 30–90 minuti al giorno.
• Questo provoca una mobilizzazione dolce e un sollievo della pressione sui nervi che innervano gli organi pelvici.
Cosa succede nel corpo:
• Migliora l’innervazione segmentale
• Gli organi pelvici tornano a funzionare in modo armonico
• Il dolore al sacro, SI o glutei si riduce gradualmente
Conclusione:
• Il dolore lombare ha spesso cause profonde
• Il legame con vescica, utero, prostata o retto è reale
• Il corpo segnala dove c’è squilibrio – meccanico, vegetativo o emotivo
• Con il mobiball puoi agire in modo mirato – senza farmaci, senza effetti collaterali
_____________________________________________________________________________
Français:
Quand le bas du dos lâche – Articulation sacro-iliaque, bassin et organes en interaction
De nombreuses personnes souffrent de douleurs dans le bas du dos, au niveau du sacrum ou de l’articulation sacro-iliaque (ASI). Ces douleurs apparaissent souvent d’un seul côté, irradient vers la fesse ou l’aine, et sont décrites comme un blocage ou une instabilité. Ce que beaucoup ignorent : cette région est étroitement liée aux organes internes du bassin – vessie, utérus, prostate et rectum.
Lien organique : Organes pelviens et colonne lombaire
L’innervation autonome de la vessie, de l’utérus, de la prostate et du rectum passe par les nerfs des segments L4 à S1 – c’est-à-dire de la colonne lombaire inférieure jusqu’au sacrum. Un blocage ou une tension musculaire dans cette zone peut donc entraîner à la fois des douleurs lombaires et des troubles fonctionnels des organes pelviens.
Symptômes internes possibles :
• Vessie irritable ou besoin fréquent d’uriner
• Douleurs menstruelles, tiraillements dans le bas-ventre
• Troubles de l’érection, baisse de libido
• Constipation, sensation de pression rectale
• Douleur à l’aine, agitation pelvienne
Ces symptômes ne proviennent souvent pas d’une maladie de l’organe, mais d’un dérèglement nerveux – causé par une mauvaise posture, du stress émotionnel ou un manque de mouvement dans la région lombaire.
Composante émotionnelle : sécurité, sexualité, confiance en soi
La région pelvienne symbolise :
• La confiance dans son propre corps
• La sécurité relationnelle
• La sexualité, la fertilité et l’acceptation de soi
• La capacité à “lâcher prise” – aussi sur le plan émotionnel
Le stress chronique ou les conflits intérieurs non résolus peuvent provoquer des tensions – visibles sous forme de contractures musculaires, de tensions du plancher pelvien ou de douleurs à l’ASI.
Solution physique avec le mobiball
Le mobiball est un outil simple et efficace pour l’auto-traitement de la colonne lombaire et du sacrum.
Mode d’emploi :
• Placez le mobiball entre L1 et L3, en position assise sur une chaise.
• Restez assis bien droit sur le mobiball pendant 30 à 90 minutes par jour.
• Cela permet une mobilisation douce et un soulagement des nerfs qui innervent les organes pelviens.
Effets dans le corps :
• L’innervation segmentaire s’améliore
• Les organes pelviens retrouvent un fonctionnement harmonieux
• La douleur au sacrum, à l’ASI ou aux fesses diminue progressivement
Conclusion :
• Les douleurs lombaires ont souvent des causes profondes
• Le lien avec la vessie, l’utérus, la prostate ou le rectum est réel
• Le corps s’exprime là où un déséquilibre est présent – mécanique, nerveux ou émotionnel
• Avec le mobiball, vous agissez de manière ciblée – sans médicament, sans effet secondaire